Leads4Pas Oracle 1Z0-1084-21 dumps the latest update
The latest update of leads4pass Oracle 1Z0-1084-21 dumps test questions, all test questions and answers have been verified by Oracle experts, and are 100% authentic and effective. leads4pass 1Z0-1084-21 dumps have two modes, PDF and VCE, which can be selected at will Guarantee 100% pass,
participate in the leads4pass 1Z0-1084-21 dumps plan to ensure the first exam pass,
get 1Z0-1084-21 dumps PDF and VCE: https://www.leads4pass.com/1z0-1084-21.html (Total Questions: 72 Q&A)
Give away! Oracle 1Z0-1084-21 exam PDF download online
Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EiK9TpyqzV-0xK7amIdRFnm2hkgl6mQP/view?usp=sharing
Participate in Oracle 1Z0-1084-21 free dumps test
The answer is announced at the end of the article
QUESTION 1
You want to push a new image in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Registry. Which two actions do you need to
perform?
A. Assign a tag via Docker CLI to the image.
B. Generate an auth token to complete the authentication via Docker CLI.
C. Generate an API signing key to complete the authentication via Docker CLI.
D. Assign an OCI defined tag via OCI CLI to the image.
E. Generate an OCI tag namespace in your repository.
You use the Docker CLI to push images to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Registry. To push an image, you first use the
docker tag command to create a copy of the local source image as a new image (the new image is actually just a
reference to the existing source image). As a name for the new image, you specify the fully qualified path to the target
location in Oracle Cloud Registry where you want to push the image, optionally including the name of a repository. for
more details check the below link
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Registry/Tasks/registrypushingimagesusingthedockercli.htm
QUESTION 2
You are developing a serverless application with Oracle Functions and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage- Your
function needs to read a JSON file object from an Object Storage bucket named “inputbucket” in compartment “qacompartment”. Your corporate security standards mandate the use of Resource Principals for this use case. Which two statements are needed to implement this use case?
A. Set up a policy with the following statement to grant read access to the bucket:allow dynamic-group read-file-dg to
read objects in compartment qa-compartment where target .bucket .name=\\’ input-bucket *
B. Set up the following dynamic group for your function\\’s OCID: Name: read-file-dg Rule: resource.id =
`ocid1.fnfunc.oc1.phx.aaaaaaaakeaobctakezjz5i4ujj7g25q7sx5mvr55pms6f4da\\’
C. Set up a policy to grant all functions read access to the bucket:allow all functions in compartment qacompartment to
read objects in target.bucket.name=\\’input-bucket\\’
D. Set up a policy to grant your user account read access to the bucket:allow user XYZ to read objects in compartment
qa-compartment where target .bucket, name-\\’input-bucket\\’
E. No policies are needed. By default, every function has read access to Object Storage buckets in the tenancy
When a function you\\’ve deployed to Oracle Functions is running, it can access other Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
resources. For example:
–
You might want a function to get a list of VCNs from the Networking service.
–
You might want a function to read data from an Object Storage bucket, perform some operation on the
data, and then write the modified data back to the Object Storage bucket. To enable a function to access another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resource, you have to include the function in a dynamic group, and then create a policy to grant the dynamic group access to that resource. https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/enus/iaas/Content/Functions/Tasks/functionsaccessingociresources.htm
QUESTION 3
You created a pod called “nginx” and its state is set to Pending. Which command can you run to see the reason why the “nginx” pod is in the pending state?
A. kubect2 logs pod nginx
B. kubect2 describe pod nginx
C. kubect2 get pod nginx
D. Through the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console
Debugging Pods
The first step in debugging a pod is taking a look at it. Check the current state of the pod and recent events
with the following command:
kubectl describe pods ${POD_NAME}
Look at the state of the containers in the pod. Are they all Running? Have there been recent restarts?
Continue debugging depending on the state of the pods.
My pod stays pending
If a pod is stuck in Pending it means that it can not be scheduled onto a node. Generally this is because
there are insufficient resources of one type or another that prevent scheduling. Look at the output of the kubectl
describe … command above. There should be messages from the scheduler about why it can not schedule your pod.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/debug-application-cluster/debug-pod-replication-controller/
QUESTION 4
You are tasked with developing an application that requires the use of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
APIs to POST messages to a stream in the OCI Streaming service.
Which statement is incorrect?
A. The request must include an authorization signing string including (but not limited to) x-contentsha256, content-type, and content-length headers.
B. The Content-Type header must be Set to application/j son
C. An HTTP 401 will be returned if the client\\’s clock is skewed more than 5 minutes from the server\\’s.
D. The request does not require an Authorization header.
Emits messages to a stream. There\\’s no limit to the number of messages in a request, but the total size of a message
or request must be 1 MiB or less. The service calculates the partition ID from the message key and stores messages
that share a key on the same partition. If a message does not contain a key or if the key is null, the service generates a
message key for you. The partition ID cannot be passed as a parameter. POST /20180418/streams//messages Host:
streaming-api.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com { “messages”: { { “key”: null, “value”:
“VGhlIHF1aWNrIGJyb3duIGZveCBqdW1wZWQgb3ZlciB0aGUgbGF6eSBkb2cu” }, { “key”: null, “value”:
“UGFjayBteSBib3ggd2l0aCBmaXZlIGRvemVuIGxpcXVvciBqdWdzLg==” } } } https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/enus/iaas/api/#/en/streaming/20180418/Message/PutMessages
QUESTION 5
Per CAP theorem, in which scenario do you NOT need to make any trade-off between the guarantees?
A. when there are no network partitions
B. when the system is running in the cloud
C. when the system is running on-premise
D. when you are using load balancers
CAP THEOREM
“CONSISTENCY, AVAILABILITY and PARTITION TOLERANCE are the features that we want in our
distributed system together” Of three properties of shared-data systems (Consistency, Availability and tolerance to network Partitions) only two can be achieved at any given moment in time.
QUESTION 6
Which statement accurately describes Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Load Balancer integration with OCI Container
Engine for Kubernetes (OKE)?
A. OKE service provisions an OCI Load Balancer instance for each Kubernetes service with LoadBalancer type in the
YAML configuration.
B. OCI Load Balancer instance provisioning is triggered by OCI Events service for each Kubernetes service with
LoadBalancer type in the YAML configuration.
C. OCI Load Balancer instance must be manually provisioned for each Kubernetes service that requires traffic
balancing.
D. OKE service provisions a single OCI Load Balancer instance shared with all the Kubernetes services with
LoadBalancer type in the YAML configuration.
If you are running your Kubernetes cluster on Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes (commonly known as OKE), you
can have OCI automatically provision load balancers for you by creating a Service of type LoadBalancer instead of (or in addition to) installing an ingress controller like Traefik or Voyage YAML file
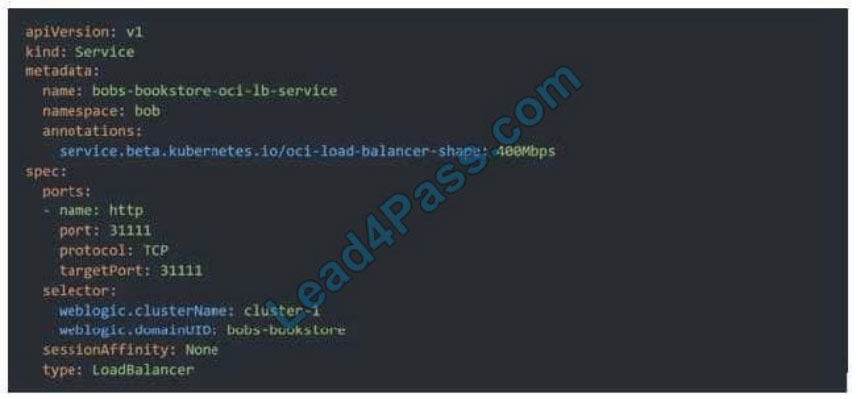
When you apply this YAML file to your cluster, you will see the new service is created. After a short time (typically less
than a minute) the OCI Load Balancer will be provisioned.
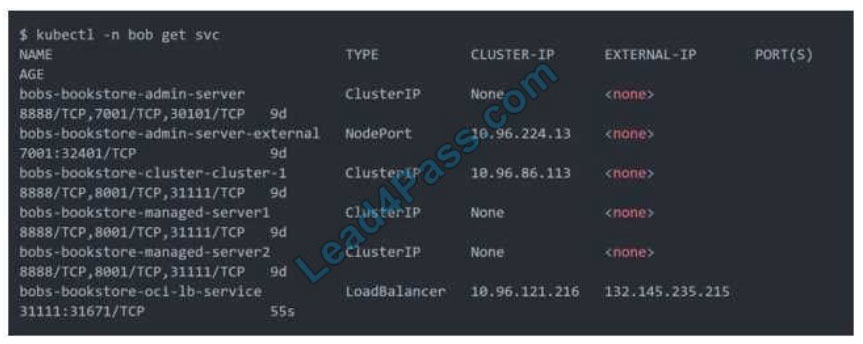 https://oracle.github.io/weblogic-kubernetes-operator/faq/oci-lb/
https://oracle.github.io/weblogic-kubernetes-operator/faq/oci-lb/
QUESTION 7
Which is NOT a supported SDK on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)?
A. Ruby SDK
B. Java SDK
C. Python SDK
D. Go SDK
E. .NET SDK
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/API/Concepts/sdks.htm
QUESTION 8
Which pattern can help you minimize the probability of cascading failures in your system during partial loss of
connectivity or a complete service failure?
A. Retry pattern
B. Anti-corruption layer pattern
C. Circuit breaker pattern
D. Compensating transaction pattern
A cascading failure is a failure that grows over time as a result of positive feedback. It can occur when a portion of an
overall system fails, increasing the probability that other portions of the system fail. the circuit breaker pattern prevents
the service from performing an operation that is likely to fail. For example, a client service can use a circuit breaker to
prevent further remote calls over the network when a downstream service is not functioning properly. This can also
prevent the network from becoming congested by a sudden spike in failed retries by one service to another, and it can
also prevent cascading failures. Self-healing circuit breakers check the downstream service at regular intervals and
reset the circuit breaker when the downstream service starts functioning properly.
https://blogs.oracle.com/developers/gettingstarted-with-microservices-part-three
QUESTION 9
How can you find details of the tolerations field for the sample YAML file below?

A. kubectl list pod.spec.tolerations
B. kubectl explain pod.spec.tolerations
C. kubectl describe pod.spec tolerations
D. kubectl get pod.spec.tolerations
kubectl explain to List the fields for supported resources
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/generated/kubectl/kubectl-commands#explain
QUESTION 10
You are working on a cloud native e-commerce application on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Your application
architecture has multiple OCI services, including Oracle Functions. You need to trigger these functions directly from
other OCI services, without having to run custom code. Which OCI service cannot trigger your functions directly?
A. OCI Events Service
B. OCI Registry
C. OCI API Gateway
D. Oracle Integration
Oracle Functions is a fully managed, multi-tenant, highly scalable, on-demand, Functions-as-a- Service platform. It is
built on enterprise-grade Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and powered by the Fn Project open source engine. Use Oracle
Functions (sometimes abbreviated to just Functions) when you want to focus on writing code to meet business needs.
The serverless and elastic architecture of Oracle Functions means there\\’s no infrastructure administration or software
administration for you to perform. You don\\’t provision or maintain compute instances, and operating system software patches and upgrades are applied automatically. Oracle Functions simply ensures your app is highly-available, scalable, secure, and monitored. With Oracle Functions, you can write code in Java, Python, Node, Go, and Ruby (and for advanced use cases, bring your own Dockerfile, and Graal VM).
You can invoke a function that you\\’ve deployed to Oracle Functions from:
–
The Fn Project CLI.
–
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure SDKs.
–
Signed HTTP requests to the function\\’s invoke endpoint. Every function has an invoke endpoint.
–
Other Oracle Cloud services (for example, triggered by an event in the Events service) or from external services. so
You can then deploy your code, call it directly or trigger it in response to events, and get billed only for the resources
consumed during the execution. Below are the oracle services that can trigger Oracle functions -Events Service
-Notification Service -API Gateway Service -Oracle Integration service(using OCI Signature Version 1 security policy) so
OCI Registry services cannot trigger your functions directly
QUESTION 11
A developer using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) API Gateway must authenticate the API requests to their web
application. The authentication process must be implemented using a custom scheme which accepts string parameters
from the API caller. Which method can the developer use In this scenario?
A. Create an authorizer function using request header authorization.
B. Create an authorizer function using token-based authorization.
C. Create a cross account functions authorizer.
D. Create an authorizer function using OCI Identity and Access Management based authentication
Having deployed the authorizer function, you enable authentication and authorization for an API deployment by
including two different kinds of request policy in the API deployment specification: An authentication request policy for
the entire API deployment that specifies:The OCID of the authorizer function that you deployed to Oracle Functions that will perform authentication and authorization.The request attributes to pass to the authorizer function.Whether
unauthenticated callers can access routes in the API deployment. An authorization request policy for each route that
specifies the operations a caller is allowed to perform, based on the caller\\’s access scopes as returned by the
authorizer function. Using the Console to Add Authentication and Authorization Request Policies To add authentication
and authorization request policies to an API deployment specification using the Console: Create or update an API
deployment using the Console, select the From Scratch option, and enter details on the Basic Information page. For
more information, see Deploying an API on an API Gateway by Creating an API Deployment and Updating API
Gateways and API Deployments. In the API Request Policies section of the Basic Information page, click the Add button
beside Authentication and specify: Application in : The name of the application in Oracle Functions that contains the
authorizer function. You can select an application from a different compartment. Function Name: The name of the
authorizer function in Oracle Functions. Authentication Token: Whether the access token is contained in a request
header or a query parameter. Authentication Token Value: Depending on whether the access token is contained in a
request header or a query parameter, specify:
Header Name: If the access token is contained in a request header, enter the name of the header. Parameter Name: If
the access token is contained in a query parameter, enter the name of the query parameter.
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/APIGateway/Tasks/apigatewayaddingauthzauthn.htm
QUESTION 12
You are a consumer of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Streaming service. Which API should you use to read and
process the stream?
A. ListMessages
B. GetMessages
C. GetObject
D. ReadMessages
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Streaming/Concepts/streamingoverview.htm Building consumers to
read and process messages from a stream using the GetMessages API.
QUESTION 13
Which statements is incorrect with regards to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Notifications service?
A. Notification topics may be assigned as the action performed by an OCI Events configuration.
B. OCI Alarms can be configured to publish to a notification topic when triggered.
C. An OCI function may subscribe to a notification topic.
D. A subscription can forward notifications to an HTTPS endpoint.
E. A subscription can integrate with PagerDuty events.
F. It may be used to receive an email each time an OCI Autonomous Database backup is completed.
Publish the answer
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | Q10 | Q11 | Q12 | Q13 |
| AB | AB | B | A | A | D | E | C | B | B | B | B | F |
Follow us! Get more updates. . .
Use PDF and VCE to get more 1Z0-1084-21 dumps exam questions: https://www.leads4pass.com/1Z0-1084-21.html (Total Questions: 72 Q&A)
Comments on 'Leads4Pas Oracle 1Z0-1084-21 dumps the latest update' (0)
Comments Feed
Comments are closed.